New cordless ultrasonic activator significantly improves disinfection
 The goal of root canal cleaning and shaping is the removal of vital or necrotic tissue, microorganisms, and their by-products while providing space for placing obturation material. The ultimate goal is the complete removal and disinfection of the endodontic space.
The goal of root canal cleaning and shaping is the removal of vital or necrotic tissue, microorganisms, and their by-products while providing space for placing obturation material. The ultimate goal is the complete removal and disinfection of the endodontic space.
EndoUltra™ is the only cordless, compact, battery-operated activation device capable of creating acoustic streaming and cavitation required to provide improved cleanliness, penetration, canal sealing, and the removal of vapor lock.
Studies show that conventional instrumentation leaves as much as 35% of the canal anatomy untouched. Instrumentation and irrigation, although important factors in canal disinfection, cannot in themselves be relied upon for optimal canal cleanliness. Research has also shown that irrigants are more effective when they are electro-mechanically activated. Acoustic streaming and cavitation have been proven to significantly enhance cleaning of difficult anatomy. Low frequency (sonic) oscillation (160-190Hz) is simply not sufficient in creating acoustic streaming and cavitation within the canal space.
The EndoUltra™ is the first device to utilize Vista’s (patent-pending) miniaturization of piezo energy technology. EndoUltra™ Activator 15/02 stainless steel tips release ultrasonic energy along the entire length of the tip and do not engage tooth structure. Activator tips feature depth markers at 18 mm, 19 mm, and 20 mm.
Test No. 1 materials and methods
In order to evaluate the fluid movement throughout the canal, a canal block was filled with water. Methylene blue dye was placed in the two outer openings. The canal block was sealed on the proximal openings to mimic canal pressure. Each endodontic product was activated and placed within the canal block. The simulation was recorded with a video camera.
The videos taken were analyzed through Image J to quantify the dye intensity throughout the canal (apical, middle, lateral, coronal) areas. The quantitative data was then converted into a percentage scale in order to compare the mixing of dye caused by each of the commercialized endodontic products, as well as a 15/02 millimeter hand file.
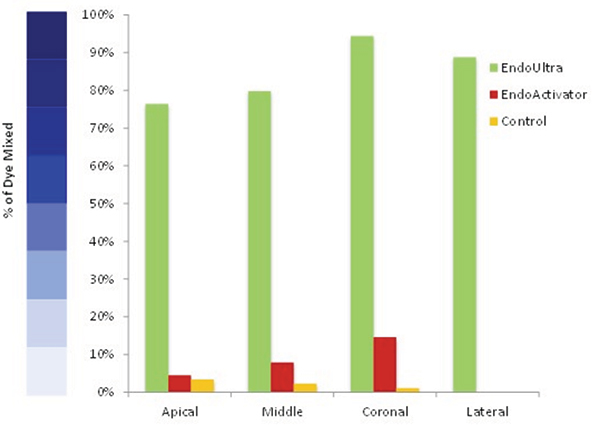
Results
The EndoUltra™ caused more mixing of the dye in the canal compared to the EndoActivator®* and 15/02 millimeter hand file after 5 seconds, and after 20 seconds of total activation within the canal.
The EndoActivator®* was unable to mix any dye within the lateral canal at either time point. The EndoActivator®* had a maximum of 15% dye that was mixed, which occurred in the coronal area of the canal. The EndoUltra™ resulted in significantly more dye mixed throughout all areas of the canal compared to the EndoUltra™ after 5 seconds and also after 20 seconds of activation.
Conclusion
In comparing two commercialized endodontic products (EndoUltra™, EndoActivator®*, and a 15/02 millimeter hand file), the EndoActivator®* and hand file were unable to sufficiently mix methylene blue dye within a canal block. The EndoUltra™ was able to mix dye within the canal block after 5 seconds of activation and produced significantly higher percentages than the EndoActivator® and hand file in all areas of the canal. Clinically, this implies that the EndoUltra™ is able to disperse irrigating solution throughout the anatomical canal to provide improved, faster cleaning of the canal and success rates compared to other endodontic devices.
Test No. 2 materials and methods
Cavitation is the generation and subsequent collapse of vapor bubbles in a solution due to localized pressure reductions. In endodontics, this change in pressure is caused by an object moving at ultrasonic frequencies. The cavitation effect can be measured quantitatively using sono-chemistry. The amount of cavitation can be increased by the addition of surfactants into solution. This is due to the ability of surfactants to decrease the intermolecular forces between water and solute molecules.
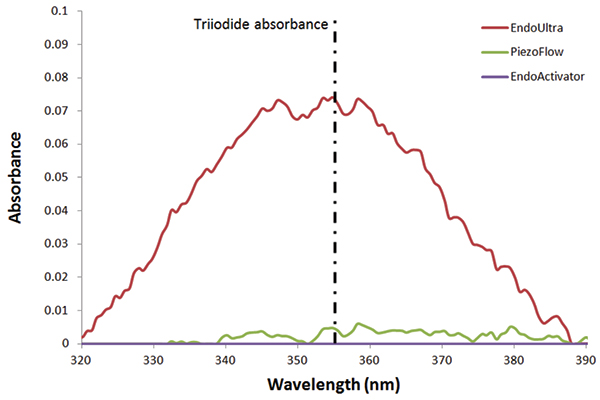
absence of absorbance at 355 nm, whereas the EndoUltra™yields significantly more cavitation and triiodide formation
Conclusion
All commercially available activation devices tested, with the exception of the EndoUltra™, were unable to produce cavitation.
For more information, call Vista Dental Products at 877-418-4782, or visit www.vista-dental.com or www.EndoUltra.com.
*EndoActivator® is a registered trademark of ENDO INVENTIONS, LLC.
This information was provided by Vista Dental Products.
Stay Relevant With Endodontic Practice US
Join our email list for CE courses and webinars, articles and more..

